Organic compounds
-carbon based molecules, also called biomolecules
The role of carbon
Carbon has 4 electrons in its outer valence shell, therefore it can form very stable compounds by covalent bonding (a very strong type of bond).
The compounds formed can range from simple molecules to very large macromolecules. They can be straight chains, branched chains or even rings, with single, double or triple bonds, therefore very diverse C skeletons.
Image from www.contexo.info/DNA_Basics/Cell_Chemistry.htm
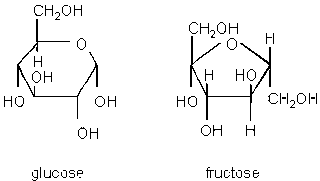
Isomers increase diversity. Isomers are compounds with the same atoms (chemical formula), but different 3D structures eg. glucose and fructose.
Image from faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/michael.gregory/files/bio 101/bio 101 lectures/biochemistry/biochemi.htm
How large compounds are formed
Monomers are smaller organic compounds which form the basis for the larger compounds. They are often bound together in repetitive chains, therefore they are called the subunits of the larger compounds.
The larger compounds are called polymers.
Starch and glycogen are polymers made of many glucose monomers.
Polymers are formed by condensation reactions.
Hydrolysis breaks down polymers into monomers.
Images from www.bio.miami.edu



No comments:
Post a Comment